 Image credit: Giovanni Pecoraro
Image credit: Giovanni PecoraroAbstract
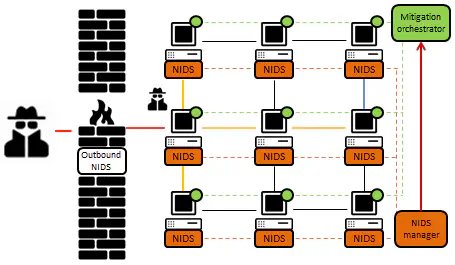
The fast evolving nature and the growing complexity of modern offensive techniques used in Advanced Persistent Threats attacks call for innovative approaches for defense techniques. The ability of modern offensive operations to acquire a foothold and then expand an infection inside the victim’s local area network, usually referred to as lateral movement activity, is significantly critical. Not only a distributed monitoring infrastructure is necessary to overcome the lack of a single network point for detection (opposed to the traditional network perimeter defense relying on outbound network intrusion detection systems), but also new signatures appear necessary to model the stealthy and complex behavior of offensive lateral movement activities. In this paper we demonstrate how to effectively use eXtended Finite State Machine patterns to face a set of commonly used lateral movement techniques. With reference to real world lateral movement attacks (including those ones based on IP spoofing), we show how the relevant detection signatures can be gathered and formally modeled, also employing a widespread distributed security architecture. Numerical results on real world traces show the effectiveness of the proposed approach in avoiding false positives.